Anyone who follows this blog knows that last May, Amazon drastically changed their popularity lists (available on the left sidebar of the main Kindle store) to change the way free downloads were factored into the ranks. On last week’s Self-Publishing Podcast #42, I was asked whether this change was done in order to present readers with better books.
The short answer: yes.
The longer answer: not necessarily better books, but certainly more profitable ones. That’s a very important distinction to make right off the bat. In all media, there’s an ongoing, centuries-long debate about whether a work’s value is based on its commercial appeal or its artistic qualities. As it turns out, I have nothing to contribute to that debate. So what follows should in no way be taken as a judgment of books that have failed to thrive under the recent Select model. Some of my books did worse as well.
But here’s what we know. Between the birth of the Select program in December 2011 and mid-March 2012, all it took for a book to hit the first few pages of its category after a free run was a few hundred downloads. 2000+ would essentially guarantee you’d be near the top of your category, probably for 2-5 days. Because a free download was weighted the same as a paid sale. And very few books are currently selling hundreds of copies per day on Amazon. Right now, about 1000 sell 100/day. Maybe 500 sell 200/day. And only something like 100 sell 500+/day. The numbers were a little lower a year ago, but not by all that much.
Meanwhile, every day, freebie aggregate blogs were pointing their readerships toward several dozen free titles. The biggest blogs had tens of thousands of subscribers, more or less guaranteeing every book featured would pick up at least 1000 downloads. There was some level of curation involved–covers had to be at least halfway decent, and there was typically a rating threshold of some kind–but the blogs had no real way to test the commercial potential of the books they mentioned. And when a book is free, the resistance to downloading it is much, much lower than when that book has a price tag attached to it.
The result is that a lot of books with lower commercial appeal wound up displacing books with higher commercial appeal. On Amazon’s popularity lists, 1000 free downloads beat 100 paid sales, and new Select books were picking up thousands of free downloads every single day. The gatekeepers weren’t strong enough to keep out the low-appeal books, meaning readers were less likely to buy the books in front of them or to be satisfied with the titles they did purchase.
What was the solution? Well, Amazon wasn’t about to start curating these books themselves. Amazon is all about letting massive numbers of consumers reach their own decisions, proving in the most meaningful possible fashion which books have the highest commercial appeal. So some churn of their lists was probably a good thing, as it broke up the stagnation of long-term bestsellers (by the way, the iBookstore is currently struggling with this problem) and presented more voracious readers with fresh material. But this was too much, and it was too unregulated.
The answer was to raise the standards for which books would get prime placement. And in typical Amazon fashion, they would tie that standard to consumer behavior.
In March, they started testing new popularity lists; in May, there was a new algorithm. The winner no longer weighted free downloads equally with paid sales, but at something near a 10:1 scale. And instead of weighting the last 1-7 days of sales + downloads, it looked at the last 30.
So instead of needing 2000+ downloads to land high on the charts–a number most decent-looking books promoted by the top sites could cross; about 100 free books managed that number of downloads per day–their new formula required somewhere between 8000-20,000 downloads to really hit it big. The more niche or iffy books couldn’t hit those numbers anymore; fewer than twenty per day could climb those heights. With exceptions, the only books that could rake in that many downloads were the ones that would have guaranteed commercial appeal when plunked in front of readers. The gatekeepers–readers, making their download decisions one click at a time–were made stronger.
They crowdsourced commercial appeal. In the environment of the time, one or two or three thousand readers downloading a free book wasn’t a terribly accurate predictor of that book’s potential. But if you upped those numbers ten times over–to ten or twenty or thirty thousand reader downloads–you had a much more accurate barometer for which books would sell when they were awarded with extra visibility.
It was a net gain for readers, who had an easier time finding appealing books, but a net loss for writers, fewer of whom could pull in the number of downloads required to hit the jackpot.
Again, I’m presenting this without judgment. A book’s surface appeal, which prompts free downloads, doesn’t necessarily represent its deeper appeal, which prompts word of mouth and long-term sales (to say nothing of literary or artistic appeal). And Amazon’s current algos aren’t perfect. Certain factors–the readership demographics of the major blogs, crossover appeal of the larger genres, Amazon’s categories, etc.–means that certain subgenres (romance, thrillers, etc.) have an easier time of it than more niche subgenres (epic fantasy, Westerns?, etc.).
This is just my narrative of what happened. Amazon’s standards/algos weren’t high enough to deal with the emerging free book market; the rewards for making your book free were disproportionately high compared to their average commercial value.
So they raised their standards. And a lot of authors were left scrambling for a new solution.
~
The silver lining to these changes is that we as authors can take advantage of the raised standards to gauge the appeal of our own books. But since this post is already closing in on 1000 words long, I’m going to tackle that in a followup.
But not by me! Now that’s a good bait and switch. Instead, check out this post by Phoenix Sullivan. In it, she explains the difference between Amazon’s bestseller list and the popularity list, as well breaking down the mechanics of the way the popularity lists currently work. There’s a bit of math, but it’s laid out quite simply. Also there are words that you can read. Which you should go do now. Enjoy.
So when we last left off, Breakers‘ free days had rolled off its popularity list rankings. That process took three days to finish (since it had been free for three days). Within a week, its sales had dwindled from 50-70/day to 10/day. I still had decent pop list placement, because it had sold so many copies in the last 30 days, but as each day passed, its pop rank continued to slide, because the old high-sales days were being replaced by new low-sales days. The end was night.
All the while, I was having a pretty obvious thought. If a big free run had propped it up in the first place, what if I did another free run? I probably couldn’t match my previous total giveaway numbers, but if I made it free while it still had a lot of paid sales credited to it, would that be enough to boost me back up the lists and continue the ride for another thirty days?
Meanwhile, I was having a second, far less reliable thought, because my brain can’t leave well enough alone. The thing is, Breakers was outselling a lot of the big sci-fi books around it on the pop list. Its bestseller rank was consistently better than Ender’s Game, for goodness sake. If the pop lists were calculated purely by sales, it wouldn’t have fallen off at all. The only reason it did drop relative to these other books was because they were priced higher, and ever since the beginning of May, price is weighted heavily in how the pop lists are ranked.
So what if I raised the price, too? Before, I was selling at $3.99. Would my sales hold steady (or close to it) at, say, $5.99? If so, when my latest free run ran out in another 30 days, would I be able to avoid eating cliff? Or at least suffer a less painful, more gradual decline?
So I set it free again. For two days. That was all the days I had left. And I waited to see what would happen.
And then Amazon botched my promo.
Instead of starting on June 23rd as scheduled, Breakers didn’t wind up going free until around 2 AM June 24th. I emailed KDP and called AuthorCentral (KDP has no phone number), but KDP was no help. That left me with just under one day to get as many downloads as I could. When it finally did go free, things went about as well as I could have hoped–POI picked me up, and so did ENT–and I finished the day with about 5600 downloads. On the one hand, that was really good, but on the other hand, with another day, I probably would have finished with between 8000-10,000. I needed every one I could get to restore my lost placement.
In the end, it wasn’t quite enough. I bounced back up the pop lists, but not as high as before. Initial sales were pretty good (25-30/day), but even at the higher price, it wasn’t enough boost to keep up with the higher-sales days of 30 days ago that were continuing to roll off my rank. I think my worse bestseller rank was hurting me here, too, but it’s really hard to say. Sales held steady for about ten days, then halved after July 4.
Since that end of the experiment was a bust, I decided to learn what would happen if I raised the price to $7.99. Interestingly, sales held steady around 10/day for another couple weeks. Three weeks out, they halved again. A few hours ago, Breakers ate cliff again, falling from #27 in Science Fiction > Adventure to #113. I’m guessing its sales are going to be pretty slow from now on. (Well, until more magic happens, anyway.)
For all I know, the higher price crippled its ability to stay as sticky this time, too. But I don’t think that’s the only factor. Over the last couple months, I’ve watched several books try this same trick–doing regular free runs to prop up their pop list rank for another 30 days. Every time, they don’t come back as strongly as before. Don’t get me wrong, they still do very well–coming back at #1500 instead of #500, say, or #2200 instead of #1500–but there is, in this limited sample size, a clear trend of diminished returns.
What’s happening? Are these books, including Breakers, slowly exhausting their audiences, even with similar pop list placement as before? Is it the case that, after an initial giant free run, a book is essentially experiencing what it’s like to be a popular new release, and when it pops back up after its first cliff, it’s being met with a lot of eyes that have already seen it?
Likewise, these books’ second and third big free runs are never as big as their first. Not that I’ve seen, anyway. The obvious conclusion–which isn’t to say the correct one, necessarily–is that they’re draining the well, so to speak. Massive free runs depend on just a handful of sites. Once you’ve tapped those sites once, the well has that much less water in it the next time you return. It refills over time as new subscribers sign up, but in my observation, it doesn’t refill completely within 30 or even 60 days. In fact, it may take much longer than that.
We’re back in the realm of speculation now. But the logical conclusion is this that riding free runs every 30-40 days can be an effective strategy (although ENT now says they won’t mention a book within 60 days of the last time it was free, meaning you’re basically down to POI, FKBT, and paid ads for exposure). This can last for several months, anyway. But it appears to be less effective the more you do it, and there is a point where a diminished 30 days of sales + a diminished free run isn’t going to be enough to prop you up to a significant place on the pop lists. When that happens, the run’s going to be over for a while. At least until the wells refill. Or you discover some other way to get your book back up there.
There’s also the question of whether giving away that many books might hurt your long-term sales. I have no answers to that question. People are buying their first ereaders every day. Considering there are already millions of Kindles out there, giving away 50,000 copies of your book over the course of a year may be a drop in the bucket of your potential audience. Readers aren’t a nonrenewable resource. Still, I don’t think it’s an unreasonable question, especially if you might be better served waiting to reach those readers for when you’ve got the next book in the series ready, say.
This is getting far afield. Nearly three months after the new algorithms spraing into being, here are my conclusions, which may or may not be remotely accurate:
* The Select program continues to reward far fewer books in the past
* The few books it does reward are well-positioned to continue to exploit their appeal
* If timed right, and with the right luck, these books can chain several months’ worth of strong sales together
* However, there will likely be diminishing returns after two or more of these runs, and it is unlikely to be something that can be maintained for more than a few months in a row
* While Select may no longer be very useful for most single titles, it continues to be quite useful for series
As for me, I’ll be leaving my fantasy series in Select for the time being, but I’m letting Breakers‘ Select contract expire early next month. I’d like to explore the other storefronts with a book I know is capable of selling. I’d like to see if I can build sales that are less roller-coastery. And to be perfectly frank, I’m pissed off at Amazon’s shitty customer support (grumble grumble bitch&moan). I’m sure they will be devastated to have lost my exclusivity.
What might this mean for your book? That is virtually impossible to answer. Maybe you’ll strike it rich on your next free run, but the chances of that are pretty low, unfortunately. And the strategy discussed above certainly isn’t a long-term plan (although giving away and selling that many copies may build you a readership that is very long-term indeed).
At the same time, what’s the alternative? De-enroll from Select, push the book to all the other stores, and pray it catches on? That’s not exactly an active strategy. Yet the other stores don’t have the same kinds of tools for discoverability that Select provides. It’s possible to make books free on iTunes and Kobo, yes, but that doesn’t result in the same list placement going free provides on Amazon. (Well, it kind of does on iTunes, but it’s clumsier, it takes much, much longer, and it’s far from guaranteed.)
In other words, we’re still in the same boat we’ve been in since mid-March. Select doesn’t sell like it used to, but the other sites are a cross between a roulette wheel and a wasteland. I’m growing restless and disillusioned, so I’m going to go exploring. I don’t know what you should do, but I’ll report back with anything interesting I find along the way.
Last time I looked at Amazon’s current algorithms, I speculated what would happen 30 days after Breakers‘ giant free run. At that point, all the free copies it gave away would stop counting towards its rank on the popularity lists. That was a frightening prospect, but at the same time, I’d racked up some 2300 paid sales (and another 600 borrows) in the 30 days since my giveaway. Would those be enough to sustain my place on the pop lists? If not, what would happen? Would I face a slow decline, or a swift one? Would I stroll down a hill, or smash down a cliff?
Well, here’s a look in chart form. Here’s Breakers‘ entire sales history:
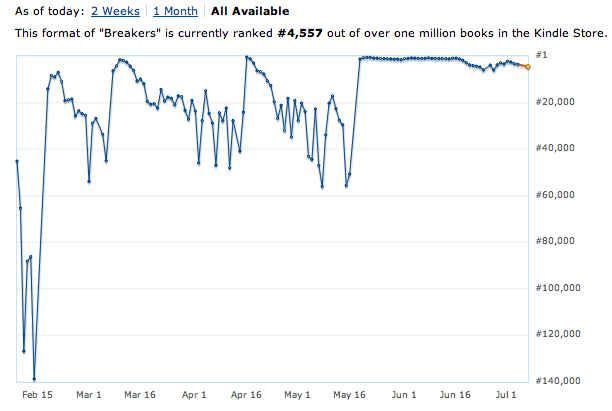 |
| Pictured: D’oh |
That doesn’t look so bad. That nice, flat line goes on forever and ever. It’s just a little jagged there at the end is all. Wait, let’s take a closer look:
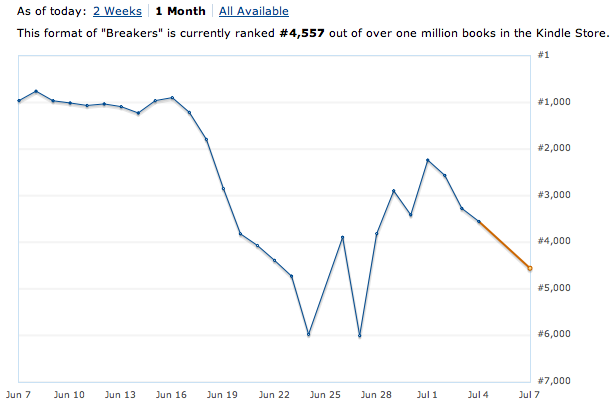 |
| Pictured: D’oh, Part 2 |
Okay, that’s a better look at what happened. What we’re seeing here is twofold. First, notice that downward slope starting around June 16? That’s when my free days stopped counting. The descent was swift–nearly 1000 ranks a day until I hit #4000, when the decline slowed. That is not a gentle hill. That is a brutal cliff. The drop from #1000 Paid to #2000 Paid is the difference between roughly 70 sales per day and about 40 sales/day. And rank declines more slowly than it rises, meaning my drop was even stiffer than that. Within a week of my free days beginning to roll off, I’d dropped from #1000 to #5000. In terms of daily sales, that was a drop from 50-70/day to 10/day.
I had braced myself for it, but it’s hard to brace yourself for a freefall. Mostly what happens at the end of the cliff is a puddle composed of you.
“But wait,” you say. “Bottoming out at #6000 isn’t so bad. That’s a pace around 500 sales/month. And anyway, rank spiked just a few days after that, taking you back to #2000. What are you bitching about?”
What am I–? Look, we’ll get to that in a moment, Captain Impatience. First, I want to talk about the why some more. Why such a steep decline? After all, my bestseller rank was still really good. #1000 overall, which was something like #8 in Technothrillers and #22 in Science Fiction > Adventure. That’s quite a bit of visibility, isn’t it? And what about also-boughts? At that point, I had a lot of popular sci-fi books pointing back to Breakers in the form of the “Customers Who Bought This Item Also Bought” lists.
Well, it turns out those things just aren’t all that important. Ha ha! That is way too flippant of an answer. Totally misleading. In truth, bestseller rank and alsobots clearly matter to some degree, but the more I do this, the more dismissive I am of them in general: while they certainly help generate sales, the bestseller lists are so volatile your book can sink extremely rapidly, and the alsobots are such a harsh filtering process (basically, your book needs to be on the first page of a book that has just been finished by a reader who is interested in buying another book right now) that they are of limited use. I think if you have a very high bestseller rank, or first-page placement on the alsobots of a very popular book, then that can do a lot for your sales, but otherwise, those are the supporting cast to a book’s sales, not the star.
The star is the popularity lists. And your book isn’t on just one of them, it’s on a bunch. For instance, one of Breakers‘ category paths is Kindle Store > Kindle eBooks > Science Fiction > Adventure. Each of those is a separate popularity list, which means the book is listed (somewhere) on each of them. Say it’s showing up at #20 on > Adventure; that would place it somewhere around #40-50 in > Science Fiction, and somewhere like #1200-1600 in > Kindle eBooks. In terms of discoverability, it would be very easy to find in SF > Adventure (second page), pretty easy to find in > Science Fiction (page 4-5), and totally awful in > Kindle eBooks (page 100+). No one is going to click through 100 pages in the eBooks category to find it. But this is part of the reason mega-popular books like 50 Shades of Grey or The Hunger Games stay so sticky for so long: when you’re #1 in the store, everyone sees you every time they visit Amazon. Plus the whole “world-destroying word of mouth” thing. But extreme visibility in high-traffic categories leads to a lot of clicks on your book, which in turn generally leads to a lot of sales.
That’s essentially why Select free runs used to do so well on the old pop lists. And that’s why taking a sudden tumble from, say, #10 in > Science Fiction (where I peaked)–the first page of the entire category–to #40-50 or wherever makes such a big difference. And remember, you’ve got another subcategory you’re listed on, too. Once your visibility is lost when a big free run rolls beyond the pop list window, you’re not going to regain it without another push.
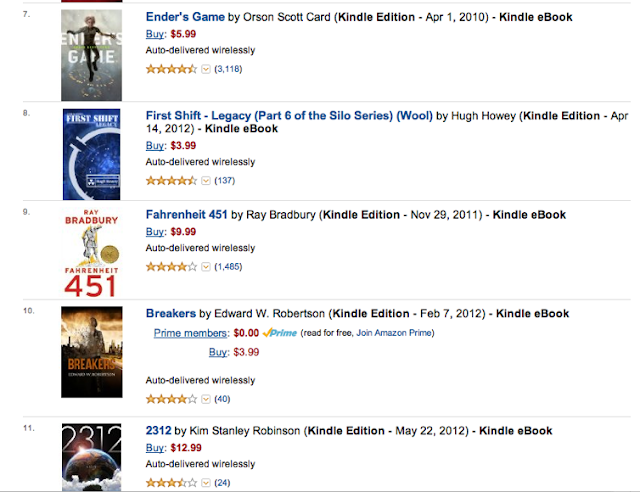 |
| Breakers’ peak rank on the Science Fiction popularity list a week before I ate cliff |
As the headline says, I’ve been interviewed at Up Your Impact Factor, a blog about getting by in modern times. What do we talk about? Well, the changes to Amazon’s algorithms, of course, as well as what it means for Select.
In my last post examining the effects of a large free run under the current algorithms, I looked at how Breakers‘ sales had been in the week after giving away 25,000 copies. They looked steady. And given that the book would have very strong position in the popularity lists for 30 days, my best guess was that sales would stay strong throughout that period.
Still, that was just a guess. And I thought it was also quite possible that sales would slow. Significantly so, even–maybe regular browsers of the popularity list would all snap it up in the first few days, leaving it much more sluggish after that. There was no way to know for sure until more numbers came in.
Okay, by my count, it’s now been 17 days since Breakers reverted to paid. Here’s a look at its last 30 days of sales:
That is a line. An almost-straight one. That line represents numbers that are frankly humbling and my-mind-blowing; I’m not sure how to address this without it coming across as bragging. That line represents some 1250 sales and 400 borrows.
Yet it’s also a bit deceptive. That graph is measuring all numbers between #1 and #60,000. How does it look at a more micro level? Here’s the graph for the last two weeks:
By Authorcentral, it peaked May 22, ending the day at #550. It declined every single day after that, reaching its nadir at #1583 on May 31. On June 1, it leapt to #1099; it reached #821 by June 3, and while that graph isn’t showing its latest increase, at 12:45 PM June 5, it’s at #852.
What caused the rebound? Borrows are a big part of it. Breakers has been listed at #1 in Science Fiction in the Kindle Online Lending Library for at least a week now. Despite the top placement in its genre, in the last four days of May, Breakers had 37 borrows, averaging 9.25/day. In the first four days of June, it’s had 110–27.5/day. Clearly, most Prime members had exhausted their monthly borrows by the end of the month; as their borrow refreshed June 1, many new readers snapped up the book.
But an extra 18 borrows a day isn’t quite enough to boost it from #1600 to #800. The borrows can be explained by the start of a new month, but raw sales are also up, too, from 57.75/day in the last four days of May to 77.5/day over the first four days of June. That’s a 34% increase(?!?).
How to explain that? I don’t know. Its pop list ranks have been steady for days now. Presumably, as borrows came in, boosting Breakers‘ rank on various bestseller lists, the additional visibility led to a few more sales, but I don’t think that’s the only–or even the primary–driver of these extra sales. Its bestseller ranks haven’t rebounded that much. All I can offer on this front is conjecture: Are shoppers more free with their money early in the month? Does Amazon send out extra recommendation emails at the start of the month? It’s also gotten 23 new reviews since going free (it had just 9 before); is that helping to convince shoppers to click “buy”?
I don’t know. All I can conclude is that a free giveaway can pay off heavily in borrows as well as sales–right now, Breakers is #12 on the popularity lists in all Science Fiction, but none of the books above it are enrolled in Prime, meaning it gets the #1 spot in the KOLL. The frenetic pace of early-month borrows is already slowing, but that was a nice shot in the arm–my sale : borrow ratio is currently at almost exactly 3 : 1. I believe very few of those borrows are cannibalized sales. My gut feeling, having seen numbers on a bunch of other books, is that a more “normal” sale : borrow ratio would be more like 10 or even 20 : 1. In other words, a full ~25% of my total income so far this month is directly due to having such ridiculously high placement in the KOLL.
17 days in. That gives me another 13 before my free downloads slide beyond the 30-day window of the popularity lists. In another two weeks, then, I expect the gravy train to run out of steam. Possibly to fly off the rails altogether. But it won’t vanish from the popularity lists altogether–by then, it’ll have somewhere in the neighborhood of 2000 sales credited to its ranks, meaning it might only drop from page 1 to page 2 or 3. Even so, that could lead to a death spiral, a negative feedback loop where lower visibility –> lower sales –> even lower visibility –> even lower sales, but we’ll see.
Wherever it goes from here, I can’t consider this as anything but a success. It’s been fascinating to watch, and from a personal angle, it couldn’t have come at a better time–my fiancee’s workplace is reducing everyone’s hours, and our ability to scrape by, already rocky, might have become downright jagged. Even if it crashes and burns in another two weeks, it’s already saved our bacon.
So we’re now three weeks into Amazon’s most recent set of algorithms. I don’t know the first thing about what they’ve meant for the overall activity of the Kindle store, but in terms of books in the Select program and free giveaways, some trends are starting to emerge. And they generally aren’t too favorable.
Yet they aren’t completely disastrous, either (depending on your definition of “disaster,” anyway). Phoenix Sullivan has a week’s worth of data on ten different titles showing a 500% increase in income in the week after her most recent free runs. At the same time, she sees that it now takes a significantly higher number of downloads to see increased sales.
Over at the Kindleboards MEGA-THREAD devoted to the tracking of free data, results are kind of all over the map, but show persistent evidence of decreased post-free sales. (Link goes to results posted after the May 3 changes; when browsing, make sure to look for free runs that took place after that date.) Still, it’s also showing that post-free sales haven’t dried up completely. Meanwhile, Russell Blake, who’s been doing pretty well for himself in part due to free runs and is touch with a bunch of other authors, has mentioned post-free sales are only about 10% of what they used to be back in the glory days. In the episode of the Self-Publishing Podcast I was on, Johnny B. Truant mentioned he’d recently given away 8000 copies and seen no appreciable sales bump. After what Phoenix has termed the Golden and Silver Ages of Select, these diminished numbers are fairly discouraging.
But here’s something else that appears to be a part of the new system:
This is Breakers‘ entire sales history, dating back to its release on February 7. Now let me doctor the charts a little bit:
The two red bars mark the approximate dates of algorithm changes. 0, 1, 2 all fell during the days of List A; 3 took place during the days of List A/B/C; 4 is what we’re seeing with the most recent set. 0 was the release date. 1, 2, and 4 came after free runs. 3 was an ad/sale price promo.
The pattern’s pretty clear, right? Under the old algorithms, books would peak, then gradually decline over the next few days until they returned to Spiky Land, where sales are few and inconsistent. (My Spiky Land sales rate was generally 0-6 per day.) The trajectory looked like the flight of a lofty home run ball in reverse–a swift rise, then a steady downward slope. Since my latest free run under the new algorithms, however, the sales trajectory is more like.. the path of a torpedo. A sexy torpedo. One that doesn’t show any major signs of slowing down.
For another three weeks, anyway, which is when things will get really interesting. What’s happening here is this. Breakers gave away 2.5 shitloads of books on its last free run (where a “shitload” is defined as 10,000 copies–note that we’re using customary measurements, not the Imperial scale). Right before it was free, its popularity list rankings were #121 in Thrillers > Technothrillers and worse than #500 in Science Fiction > Adventure. Where is it now?
Technothriller isn’t the biggest category in the Kindle store, but SF > Adventure is a pretty tough one. This is the category where George R.R. Martin and Wool chew everyone else up and drool them down their sales-fattened bellies. Yesterday, Breakers was actually #12–page 1!–but a new release from Amazon’s 47North imprint vaulted ahead of it today.
Here’s the difference between the old algos (List A) and the new. When Breakers came off free, it would have vaulted to #1 in both categories. It probably had enough downloads that it would have hit page 1 of the entire Mystery & Thrillers genre. This would have produced a rush of sales (almost certainly hundreds), but after a few days, its rank would start to decay. It would get leapfrogged by the latest post-free books off big runs of their own. Within about a week–maybe two, given a giveaway of this magnitude–it would probably be back down near its former rank and sales.
If anything, the opposite is true now for big giveaways. Initially, Breakers hit Technothrillers at #12 and Adventure at #27. It hadn’t sold much over the 30 days prior to being free. 110ish copies, I think. The new pop lists look at a 30-day rolling window of sales. Once it reverted to paid, then, its pop list placement was calculated based on 25K freebies + 110 sales. But since its free run, it’s been selling 70+ copies per day. As the 30-day window advances, then, last month’s low sales days are discarded from the equation while its most recent high sales days are added to it. The result: it has steadily climbed the pop lists ever since.
By now, it’s probably about peaked. And in another 3 weeks, those 25K freebies will roll beyond the window. At that point, it will drop down the pop lists again. How much? That will be determined entirely through how many copies it sold over its new 30-day window. But if that arrow-straight sales line from its sales history holds out, we’d be talking somewhere in the neighborhood of 1500-2000 copies–in other words, enough that it’ll probably still be somewhere on page 1 of Technothrillers, and probably page 3 of SF > Adventure. That would still be a lot of pop list visibility.
In other other words, it could get sticky.
Assuming the algos don’t change over that time, of course. And that I don’t get 50 consecutive one-star reviews. And that the collective unconsciousness doesn’t decide Breakers is 300-some pages of garbage and that its author should be defenestrated with all possible haste. Or that interest doesn’t simply dry up. The U.S.S. Me could be torpedoed at any time.
Back to the big picture. In general, Select is no longer as effective at generating sales as it was just last month. The visibility produced by most giveaways is much lesser than it was before. But if you get lucky enough, that visibility will last for much longer. More visibility, more sales. While in most cases, Select is the least useful it’s ever been–and part of me isn’t happy about that at all–in certain instances, it’s become a more powerful tool than ever.
I’ve made a small edit to my first post on Amazon’s recent changes to their sales algorithms. As you’ll recall, in that post, I took a look at the three different sets of popularity lists Amazon was displaying between March 19 and May 3. To summarize, List A was Select- and indie author-friendly. List B showed signs that making your book free would be drastically less effective than it used to be. And List C looked downright draconian: even strongly-selling indie books that had never been free were ranked 15-25% worse on List C than on List B.
Originally, we thought this was because List C factored physical book copies into its ranks, inadvertently penalizing indies who predominantly sell ebooks. We were wrong. The difference appears to be about price.
I first started looking into this after Phoenix Sullivan noticed there were very few $0.99 books high on the popularity lists. (The popularity lists are the main browsable lists displayed on Amazon. For instance, the Epic Fantasy list can be seen here.) It was theorized that the new algorithms were discriminating against the $0.99 price setting, weighing $0.99 sales at a lesser value than at higher price points. I wasn’t entirely comfortable with this theory, because I generally don’t think Amazon sets their algorithms with specific goals in mind (besides “Make $, win”). So I compared hundreds of books on several different popularity lists, focusing on the lowest-priced ebook titles. Soon, I was honing in on the highest-priced books, too. Because I was seeing something very, very strange.
The higher the price, the better the book was placed on the popularity lists.
In other words, say you’ve got a $0.99 book at #10 on the Epic Fantasy list. (Popularity list, not bestseller.) Say its sales rank (bestseller list) is #1000. The books at #9 and #11, meanwhile, are both listed at $9.99–and their sales ranks will probably look more like #3000, say.
This isn’t an ironclad correlation. Bestseller rank is a transitory thing. It shifts very quickly compared to popularity rank; a book that’s #1000 today could be #1 or #10,000 tomorrow. Seeing one instance of a book outperforming its bestseller rank on the pop list ranks proves nothing.
Seeing hundreds of these instances, however, is another thing altogether.
And that’s what I saw. Repeatedly. Undeniably. It was 1 AM, I’d had a couple of drinks, and my fiancee was snoring on the couch as I nerded it up with my numbers, but what I was seeing was strong enough to not only prove the theory I’d set out to disprove, but to go one step further: all things being even in terms of sales, not only did a lower price indicate a worse position on the popularity lists, but a higher price indicated a better one.
The implications for indie authors are immediate. And not pleasant. Most indie authors price their ebooks between $0.99 – $5.99. A few brave souls and small presses price as high as $9.99, but generally speaking, $5 and under is seen as the way to reach readers who may be hesitant to take a shot on a lesser-known or completely anonymous author. But if you price at $2.99 while HarperCollins prices at $12.99, you’re going to have to sell significantly more copies to be neighbors on the popularity lists. And if you’re selling at $0.99, you’re going to have to sell very, very well to achieve the same level of visibility.
We’ve termed this change “price biasing.” Here’s what it looks like in practice. Let me show you a shot of the Epic Fantasy popularity list:
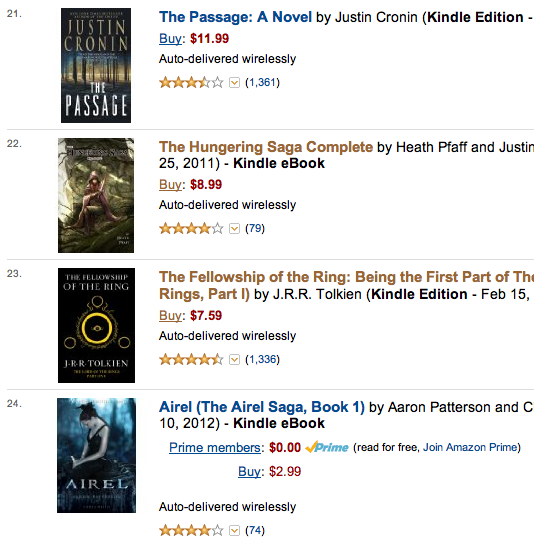 |
| Evidence of price biasing: Epic Fantasy popularity list, page 2 |
Now, here is the bestseller rank of these same titles:
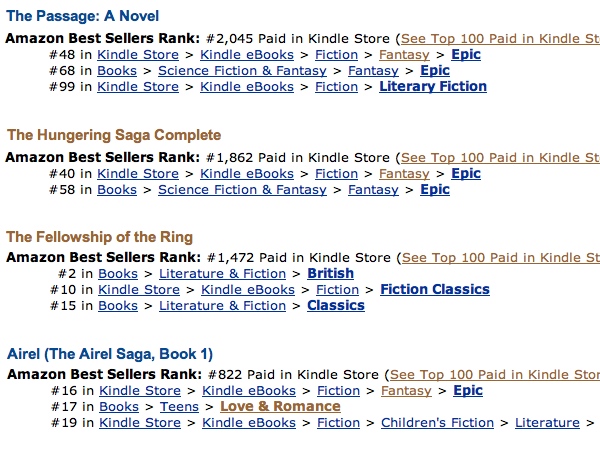 |
| Bestseller ranks of these same books |
Let’s move to the next page:
 |
| Epic Fantasy popularity list, page 3 |
And their bestseller ranks:
 |
| Bestseller ranks of these same books |
Take a look at that–in the first example, all of the higher-priced books shown are ranked above the lower-priced books on the popularity list, but their sales ranks are worse. In order! In the second example, the $0.99 book requires drastically higher sales to keep pace on the popularity lists with the $13.99 book. For another example of price biasing, simply go to the top of Epic Fantasy, where George R.R. Martin’s A Game of Thrones 4-Book Bundle, is priced at $29.99 with a bestseller rank of #60 and a popularity list rank of #1. The next book, Martin’s A Game of Thrones, is priced at $8.99, yet is #2–behind the omnibus–despite a bestseller rank of #27.
There are a lot of variables at play here. Because of the volatility of bestseller rank, I can’t be certain that the higher-priced books haven’t outsold the lower-priced ones over the last 30 days, and it will be easy enough to find counter-evidence where books are “properly” ranked and price seems to make no difference. But I’ve tried to minimize the variables by choosing books that haven’t been recently released (so sales should be steadier) and by going to page 2 and 3 of the popularity list, where the volatility should be lesser than at the very top. Really, it wasn’t hard to find this example. Because it’s all over the place. And if you look at hundreds and hundreds of titles next to each other on the popularity lists–especially the extremes, $0.99 – $2.99 books next to $12.99 – $29.99 books–the correlation is extremely high.
I don’t have the answers to a lot of the inevitable questions. I don’t know what the “ideal price” would be to take advantage of this new formula. I don’t know how many more copies you need to sell at $0.99 to achieve the same weight as you would selling at $9.99. I don’t know why Amazon did this, particularly when they price their own imprints at $7.99 and under. I don’t know if this is the end of the world or a brief couple weeks of suffering followed by another golden age.
And let’s not storm the gates or raise all our titles to $199.99 just yet. The popularity lists are far from the only driver of sales through Amazon. There are bestseller lists. Targeted emails. Bargain book lists of all shapes and sizes which you’ll only make through pricing lower. And if you raise your prices significantly enough to achieve a major change on the new popularity lists, you may drive away so many sales your placement actually winds up going down. Unless you’re priced at $0.99, I don’t think raising your price by a dollar or two will make any real difference to your placement on the popularity lists, so please don’t overreact–if you’re still selling, you’re still selling, no matter how the new algorithms may work.
Still, I don’t see how these new lists are any good for indies under any circumstances. What they do is force us to sell more books to maintain the same visibility as higher-priced trad titles. They diminish our ability to experiment with lower prices, whether the goal is a temporary sale, a low-priced entrypoint to a series, or because you just don’t feel comfortable charging more than $0.99 for that 5000-word story.
Furthermore, the playing field is no longer level. Indie authors published through KDP only earn 70% royalties at prices between $2.99 and $9.99. Yet many traditionally published books that are most benefiting from price biasing are priced at $12.99 – $14.99, with some omnibus editions priced as high as $22.99 – $29.99. If indies want to match those prices to match their visibility on the popularity lists, they’ll actually make less money with each sale than they would at $9.99. There’s no way to win.
I don’t like fearmongering. But I don’t see how it helps to sit on this information any longer. I encourage you to look at the popularity lists for yourself. Maybe I’m wrong. I’d prefer if I were. I’ll try to answer any questions in comments, but be prepared for a lot of “I don’t know.” All I know for sure is that if this analysis is correct, the deck has been stacked against us. I highly doubt it was intentional. Indies aren’t being targeted. We’re just a small part of the Amazon equation, and as Amazon attempts to maximize their revenues, I really don’t think they care who that revenue’s coming from. And remember: this is just one factor among many, many others as to how a book is seen on Amazon’s storefront. It’s not a revolution in and of itself.
But it does feel like it will have some impact on indie authors. I thought it was time to share and let everyone experiment for themselves.












